FHA Loans in 2025: What They Are, Who They’re For, and How to Qualify

FHA loans remain one of the most accessible mortgage options in 2025. Backed by the Federal Housing Administration (FHA), these government-insured loans offer low down payments and flexible credit standards.
Whether you’re a first-time buyer or someone with a lower credit score, FHA loans are built to make homeownership more achievable.
This guide breaks down FHA loans, covering eligibility, benefits, refinance options, and more.
What Is an FHA Loan?
An FHA loan is a mortgage insured by the Federal Housing Administration, a division of the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). The FHA doesn’t lend money directly—it guarantees loans made by approved lenders, which reduces the risk to the lender and helps borrowers qualify more easily.
Since 1934, FHA loans have helped millions of Americans purchase homes with modest savings, lower credit scores, or limited credit histories.
FHA Loan Facts from 2024:
- The FHA guaranteed nearly 828K loans
- The average FHA loan amount was $311,786
- The average household income for approved FHA loan applicants was just under $99K
- The average interest rate on FHA loans was 6.289%
- There were 1,271 active FHA lenders in 2024
FHA Loan Advantages
FHA loans offer unique benefits that make them especially appealing to first-time buyers or borrowers who may not meet conventional loan standards. Those include:
- Low down payment: As little as 3.5% down with a 580+ credit score.
- Lenient credit standards: Some lenders accept scores as low as 580. Some may allow scores between 500–579 with 10% down. Despite low minimums from the FHA, lenders often require higher credit scores.
- Flexible refinance options: FHA Streamline and Cash-Out refinancing make it easier to lower your rate or tap into home equity.
- Rehab financing: FHA 203(k) loans let you finance repairs or improvements with your home loan.
- Assumable loans: FHA loans can be transferred to a qualified buyer, which can be a selling advantage if interest rates rise.
FHA Loan Disadvantages
Despite their many advantages, FHA loans aren’t ideal for everyone. Here are some potential drawbacks to keep in mind:
- Mortgage insurance is mandatory: FHA loans require both an upfront mortgage insurance premium (1.75% of loan amount) and annual MIP.
- MIP duration: If you put down less than 10%, MIP lasts for the life of the loan unless you refinance into a conventional loan.
- Loan limits: In 2025, FHA limits range from $524,225 (low-cost areas) to $1,209,750 (high-cost areas) for single-family homes.
- Stricter property standards: The home must meet HUD’s minimum safety and livability guidelines.
- Primary residence only: FHA loans can’t be used for second homes or investment properties.
FHA Loan Requirements
FHA loans come with some of the most relaxed qualification guidelines in the mortgage market. Here’s a breakdown of what’s required by the FHA. Note that many lenders overlay stricter requirements.
Credit Score
- 580+: Qualifies for 3.5% down payment.
- 500–579: Requires 10% down payment.
Lender overlay: Many lenders set their own minimums, often between 580–620. Refi.com requires a 620 FICO credit score for FHA refinances.
Down Payment
- 3.5% minimum with 580+ score.
- 10% down with scores between 500–579.
- Larger down payments can reduce MIP costs over time.
- Zero from your own pocket? Down payment funds can come from gift money or eligible assistance programs.
Debt-to-Income (DTI) Ratio
- Front-end DTI (housing costs): Max 31% of gross monthly income.
- Back-end DTI (total monthly debt): Max 43% (can go higher with compensating factors).
Related: Debt-to-Income (DTI) Ratio Requirements to Refinance Your Mortgage
Employment and Income
- 2 years of stable employment or income history preferred.
- Documentation: W-2s, pay stubs, or tax returns (especially for self-employed borrowers).
Appraisal
- FHA requires a HUD-approved appraisal.
- Home must meet health and safety standards called Minimum Property Requirements (MPRs).
- Note: No appraisal required for FHA Streamline refinances.
Property & Occupancy
- The property must be your primary residence.
- Properties with up to 4 units are eligible, as long as you plan to live in one of the units.
- Condos, tiny homes, and manufactured homes are eligible.
- You must move in within 60 days of closing.
- FHA loans cannot be used for second homes or investment properties.
Types of FHA Loans
FHA offers more than just basic home purchase loans. These are the most common FHA-backed mortgage programs you might qualify for:
- FHA 203(b): Standard FHA purchase loan.
- FHA 203(k): Combines purchase and renovation costs into a single loan. Check out our guide to the FHA 203(k) to learn more.
- FHA Streamline Refinance: Fast, low-doc refi for existing FHA borrowers. Check out our guide to the FHA streamline refinance to learn more.
- FHA Cash-Out Refinance: Tap home equity up to 80% LTV. See our guide to the FHA cash-out refinance to learn more.
- FHA Energy Efficient Mortgage (EEM): Adds energy-efficiency upgrades to your mortgage.
- FHA Section 245(a): Graduated or growing payment mortgages for buyers expecting income growth.
- FHA HECM (Reverse Mortgage): For homeowners aged 62+, to convert equity into cash.
- FHA Loans for Condos: Only for condos in FHA-approved projects.
- FHA Loans for Manufactured Homes: Applies to both home and lot purchases.
- FHA Construction-to-Permanent Loan: Allows you to finance both the construction of a new home and its permanent mortgage in a single loan. Available to buyers building a primary residence.
FHA Mortgage Insurance
FHA mortgage insurance protects lenders but adds cost for borrowers. Here’s what you need to know about how it works and what it costs:
- Upfront MIP: 1.75% of the loan amount (can be rolled into the loan).
- Annual MIP: Typically 0.55% with 3.5% down on 30-year loans; ranges from 0.40% to 0.75% depending on loan size, term, and LTV.
- Duration:
- <10% down: MIP lasts for the life of the loan.
- ≥10% down: MIP lasts 11 years.
- Refunds: You may get a partial UFMIP refund if refinancing within 3 years.
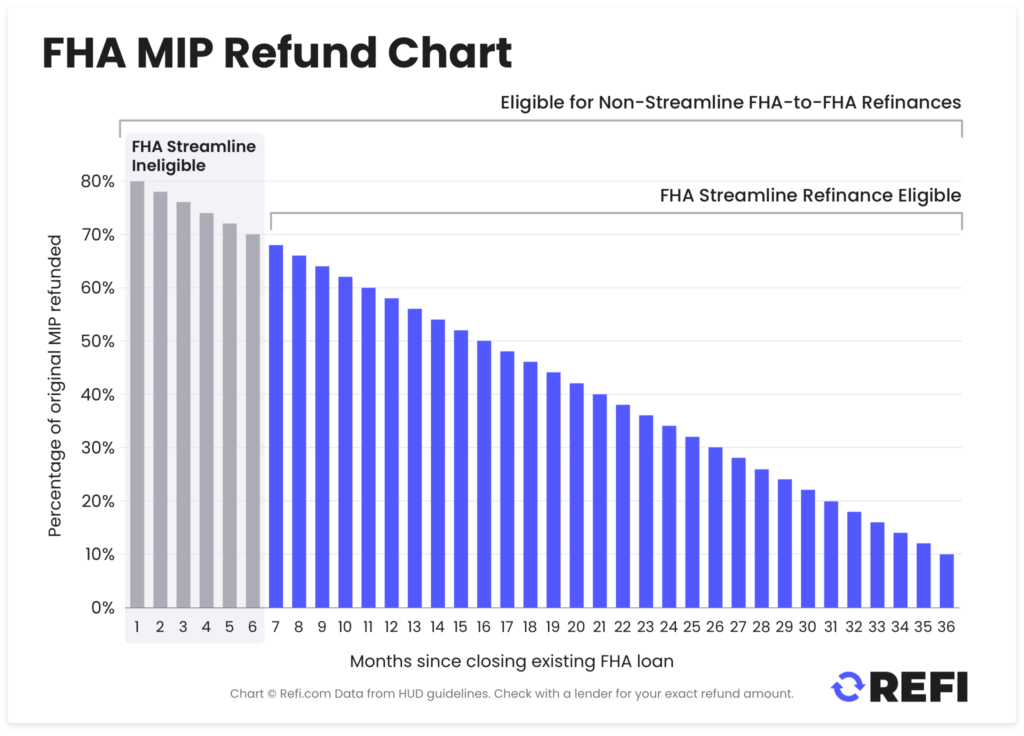
FHA Refinance Options
FHA loans don’t just make buying a home easier—they also offer great refinancing opportunities. So if you’re buying now in a high-rate environment, know that you’ll have some strategic options to lower your payment or tap your equity in the future. Here are the two main FHA refinance paths:
FHA Streamline Refinance
- No appraisal or income verification required.
- Must show Net Tangible Benefit (lower rate or more stable loan).
- Available only to current FHA borrowers.
FHA Cash-Out Refinance
- Appraisal and full income verification required.
- Max 80% LTV.
- Minimum 600 credit score (varies by lender).
If you don’t meet the requirements for a Streamline Refinance, you may still have options. FHA also offers less common refinance programs like the FHA Simple Refinance, which allows current FHA borrowers to refinance into a new FHA loan with full documentation and a new appraisal. This can be a solid alternative if you need a more traditional refinance route.
See our full guide to FHA refinance options to learn more.
FHA Loan Limits (2025)
FHA loans have maximum lending limits that vary by location and property type, and they’re generally lower than conventional loan limits. Here’s a look at the national range for 2025:
| Property Type | Low-Cost Area | High-Cost Area |
| 1-unit | $524,225 | $1,209,750 |
| 2-unit | $671,150 | $1,548,050 |
| 3-unit | $811,450 | $1,871,050 |
| 4-unit | $1,008,450 | $2,326,950 |
For specific limits by county, visit HUD’s FHA Loan Limit Tool.
FHA Loan Rates
One of the advantages of FHA loans is that they often come with lower interest rates than conventional loans. Because they’re insured by the government, lenders take on less risk—and can pass some of those savings along to borrowers in the form of more favorable rates.
However, a lower rate doesn’t always mean lower overall costs. FHA loans require both upfront and annual mortgage insurance premiums (MIP), which can add significantly to your monthly payment and total loan cost—especially if you keep the loan long-term.
Still, for borrowers with lower credit scores, FHA loans can offer more competitive pricing than conventional loans, where interest rates and private mortgage insurance costs tend to rise steeply with lower credit.
How we source rates and rate trends
Rates based on market averages as of Dec 02, 2025.Product Rate APR 15-year Fixed Refinance 5.37% 5.42% 30-year Fixed Refinance 6.35% 6.37%
FHA Closing Costs
Like any mortgage, FHA loans come with closing costs—fees paid at the time of closing that typically range from 2% to 5% of the loan amount. These can include lender fees, title charges, escrow setup, and upfront mortgage insurance.
Typical FHA Closing Costs:
- Upfront Mortgage Insurance Premium (UFMIP)
- Origination fee (charged by the lender)
- Title insurance and settlement fees
- Appraisal fee
- Credit report fee
- Prepaid property taxes and homeowners insurance
Some of these costs can be negotiated or covered by the seller through seller concessions (up to 6% of the loan amount), and the UFMIP can usually be rolled into your loan amount.
How to Apply for an FHA Loan
FHA loans are issued by private lenders, not the government. To get started:
- Choose a lender that offers FHA loans.
- Get preapproved based on your credit, income, and debt profile.
- Provide documentation and complete the full loan application process.
FHA vs. Conventional Loans
Not sure if an FHA loan is right for you? Here’s how FHA loans compare to conventional mortgages:
| FHA Loan | Conventional Loan | |
| Minimum Down Payment | 3.5% (with 580+ credit score) | 3 – 5% |
| Credit Requirements | More lenient (as low as 500) | Typically 620+ |
| Mortgage Insurance | Required upfront and annually | Required if <20% down, but cancellable |
| Property Standards | Stricter safety/livability requirements | More flexible |
| Loan Limits | Lower | Higher |
| Refinance Options | Streamline and Cash-Out | Rate-and-term and cash-out, but no streamline |
| Assumable Loan | Yes | No |
FHA loans are often the better fit for buyers with lower credit scores or limited savings. That’s because FHA loan costs—especially mortgage insurance—stay fairly consistent regardless of your credit score.
In contrast, conventional loan pricing is much more credit-sensitive. If your credit is below 700, conventional mortgage insurance and interest rates can rise quickly, making the loan more expensive overall.
Conventional loans can offer more long-term savings if you have strong credit and a sizable down payment, especially since mortgage insurance can be canceled once you reach 20% equity.
FHA Loan FAQ
Can I get an FHA loan if I’ve had a bankruptcy?
Yes. You can qualify for an FHA loan two years after a Chapter 7 bankruptcy discharge, as long as you’ve re-established good credit or chosen not to take on new debt.
For Chapter 13 bankruptcy, you may qualify after 12 months of on-time payments with court approval.
Can I use gift funds as a down payment on an FHA loan?
Yes. FHA loans allow you to use gift money from a relative, employer, or approved charitable organization for all or part of your down payment.
You’ll need to provide a gift letter and documentation showing the transfer of funds.
Can I get an FHA loan if I’ve had an employment gap?
Possibly. FHA guidelines require a two-year work history, but short employment gaps may be acceptable if you can explain the reason and show stable income now.
Lenders may ask for documentation, especially if the gap was more than six months.
Final Thoughts
FHA loans open the door to homeownership for many who might otherwise be shut out. From flexible credit requirements to low down payments and accessible refinance options, FHA loans remain one of the most consumer-friendly mortgage products available.
While they come with added costs like mortgage insurance and property eligibility standards, they’re often the best fit for first-time buyers, credit-challenged borrowers, or those refinancing an existing FHA mortgage.
Whether you’re purchasing or refinancing, FHA loans in 2025 continue to offer a reliable, flexible path to homeownership.


